‘The study of geography is about more than just memorising places on a map. It’s about understanding the complexity of our world’ Barack Obama, former US President
Geography is the study of our Earth’s landscapes, its people, places and environments. It is, quite simply, about the world in which we live. Our aim at Westhoughton High School is to develop a sense of place and to develop an awareness of contrasting physical and human environments. Geography gives an insight into the relationships between people and the environment and how each affects the other, and foster a sympathetic understanding of some of the major issues of social concern such as social challenge and urban opportunities. This aligns with our learn value to look after each other and be inclusive of beliefs and values of others.
We aim to develop skills of critical enquiry as well as a firm understanding of concepts through a variety of key questions. The opportunity for fieldwork and practical experience is seen as an important part of the learning experience to bring the concepts that we study to life and the department is committed to providing a curriculum that involves work at home and abroad. This links to our value of enjoying learning and empowering students to explore and be curious with a desire to pursue ideas and solutions and never stop learning.
We encourage all pupils to appreciate how actions and decisions made at a local level can have global implications; as a consequence, there are frequent, lively respectful discussions on themes as varied as the management and conservation of extreme environments, to the creation of sustainable communities in modern cities. We believe in the importance of this discussion and understanding in order to equip our next generations to make informed decisions for our community, country and planet. We want students to aim high, developing leadership and excellent initiative.
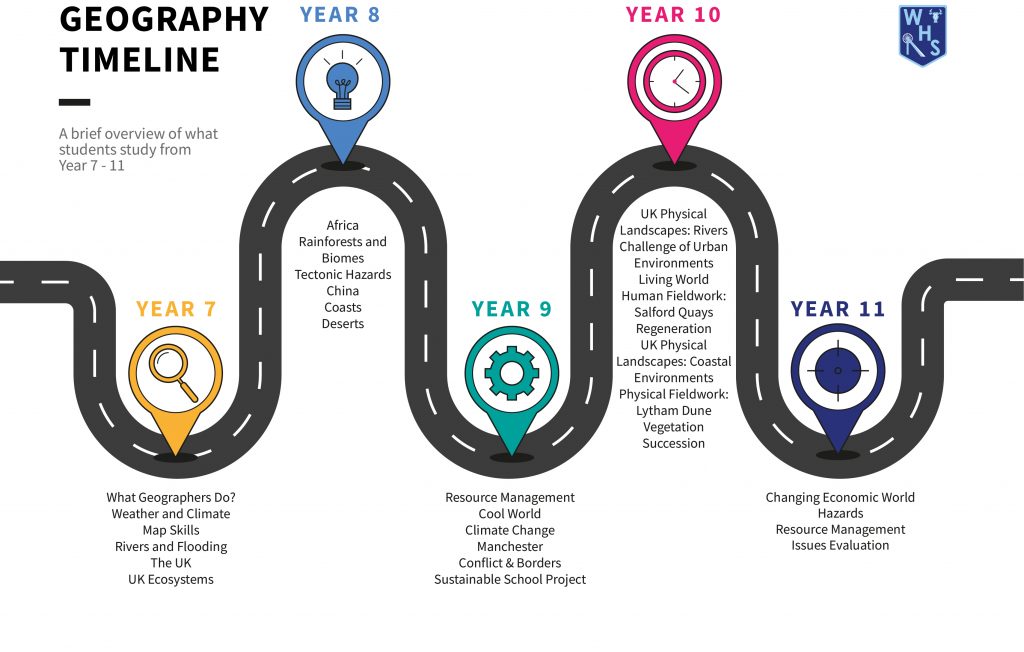
Please see parental overview of the course in KS3 and KS4 below.
Links for Support/Help at Home
- Use of student resources located within WHS SharePoint for students
- Walks and hikes to studied areas (or any areas with similar geographical landscapes/issues as studied)
- Use of additional homework booklets, therapy work packs and/or additional resources from the class teacher via Synergy
- Wider reading: library visits or non-fiction reading on landscapes or countries studied
- Use of online platforms such as Seneca for podcasts
- Watching of documentaries linked to geographical issues studied
- Teacher discussions following assessments and/or reports
- Participation in enrichment opportunities and/or extra-curricular activities